What is Search Arbitrage?
For those unfamiliar with search arbitrage, please refer to our previous article. Search arbitrage is a traffic arbitrage method involving purchasing traffic from social media/native/display/search ads and selling search ad results to profit from the difference.
Read the full article on search arbitrage:
Understanding Search Arbitrage
Demystifying Google’s Search Monetization Products
2.1 Legacy AdSense for Search (AFS)
Introduction: Google’s earliest search monetization product allowing publishers to display Google search ads on their site’s search results pages and earn revenue share.
Features:
Early Google search partnership model (Desktop-focused)
Simple monetization with limited functionality
Now replaced by AFS for Partners
2.2 AFS for Partners (AFSP)
Introduction: Upgraded AFS for large-scale search partners with flexible ad integration.
Features:
API-driven deep integration
Richer ad formats and UX optimization
Higher revenue share than legacy AFS
Effective on Desktop & Mobile (better Desktop revenue)
2.3 Online AFS Agreement Mobile
Introduction: Mobile-optimized AFS for apps/mobile sites.
Features:
Mobile-first ad formats
Compliant with mobile ad policies
Supports mobile web/app scenarios
Used by most RSoC providers (works on Desktop/Mobile)
2.4 AFD (AdSense for Domains)
Introduction: Monetizes parked domains via search ads.
Features:
For direct navigation/paid referral traffic
Displays relevant Google ads
Closed to new users since 2013 (limited partners remain)
2.5 GHS (Google Hosted Search)
Introduction: Google-hosted search solution (Custom Search Engine).
Features:
Provides site search + ad monetization
Google-hosted results (no self-built engine required)
Monetization similar to AFS
2.6 AFS Type-in / GHS Type-in
Introduction: Monetizes direct navigation traffic (users typing keywords into browsers/ISPs).
Features:
High-converting traffic
For browser partners/large traffic suppliers
This article focuses on AFS RSoC Feed relating to AFSP and Online AFS Mobile.
The Transition: AFD vs. RSoC
Google’s Policy Shifts on Parked Domains:
Oct 2024: New Google Ads accounts block parked domain ads by default.
Mar 2025: Existing accounts block parked domains unless manually opted-in.
Monthly budget removal for parked domains implemented post-March 2025.
Industry Impact:
AFD expected to phase out by end-2024 with declining RPC.
RSoC emerges as primary alternative.
Key Questions:
How many advertisers will manually opt-in?
How long will Google’s policy transition last?
Google’s Motivation:
Enhance transparency, traffic quality, UX, and advertiser trust.
Understanding Google RSoC Feed
4.1 Workflow
Social/Native/Display Ad → Content Page w/ Related Search Keywords → SERP → Advertiser Offer
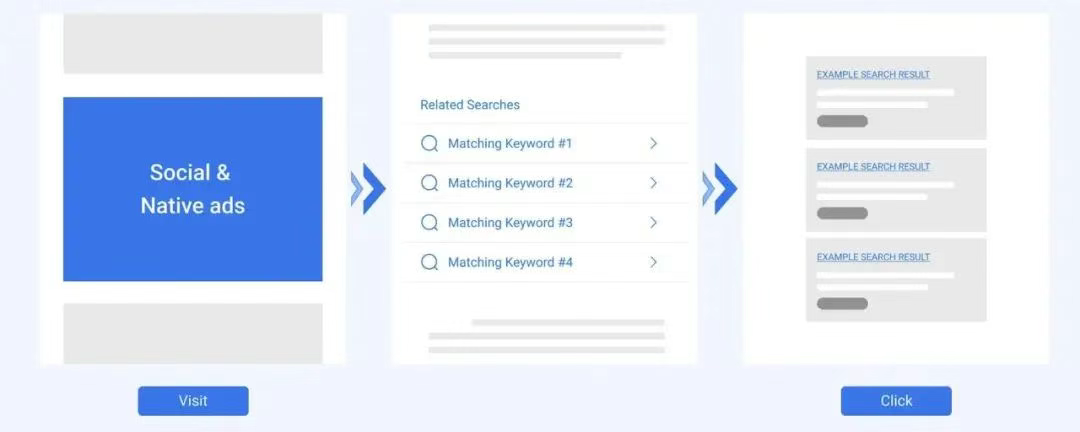
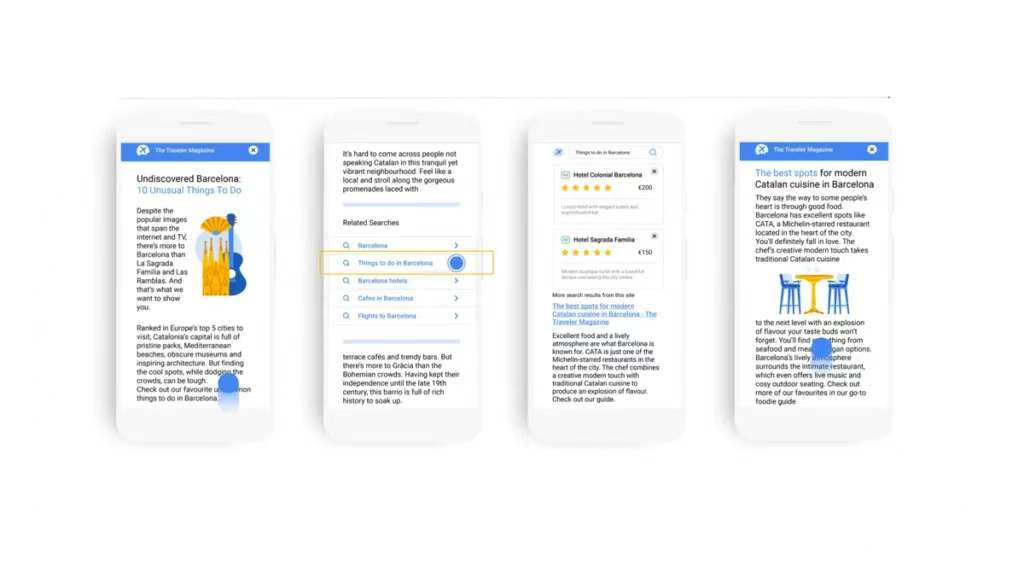
4.2 AFS vs. RSoC
RSoC embeds contextual keywords in content pages to:
Generate search intent from content browsing
Create incremental search queries
Diversify Google's search ecosystem
4.3 RSoC Advantages
Enhanced UX: Value-driven content engagement
Higher RPC: Contextually relevant ads
Diversified Revenue: Supports AdSense + affiliate offers
Sustainability: Aligns with Google's quality guidelines
4.4 RSoC Challenges
Limited Attribution:
No click-level revenue data
Revenue reported only by geo/device/channel
Channel name restrictions complicate tracking
(Solutions: ClickFlare API for estimated attribution)
Keyword Override:
Google frequently overrides preselected keywords
(Mitigation: Use 5+ long-tail keywords + content relevance)
RSoC Feed Providers
5.1 Established Providers
System1 (US): system1.com
ExplorAds (Israel): explorads.media
Inuvo (US): inuvo.com
AirFind (US): airfind.com
Intango (Israel): intango.com
5.2 Former AFD Providers (Transitioning to RSoC)
Sedo (Germany): Apply Here
Tonic (Germany): tonic.com
DomainActive (US): domainactive.com
Ads.com (US): Apply Here
5.3 Emerging Providers
BeesAds | Pubplus | AdMedia
Maximizer Rocket | Predicto
5.4 Via GCPP Partners
Affinity: affinity.com
InMobi: inmobi.com
5.5 In-House AFS Application
Requirements:
6+ months of AdSense history
Policy-compliant content
Valid search integration use case
Revenue Share: 51% of Google-recognized revenue
Payment Threshold: $100 (NET-30/45/60)
Traffic & Compliance
7.1 Approved Traffic Sources
Facebook, TikTok (non-Pangle), Google Display
(Sedo/Ads.com also allow: Taboola, Outbrain, Twitter, Snapchat, Baidu MediaGo, NewsBreak)
7.2 Traffic Quality Metrics
Spam Rate: Keep <15% (≥20% = "moderately unhealthy")
IVT (Invalid Traffic): Causes account suspensions
9.1 Core Principles
Transparency: Ad → Landing Page → SERP journey must be clear
Content Consistency: Pages must deliver ad promises
9.2 Ad Creative Restrictions
❌ Banned: Price/discount claims, medical cures, "free" offers, urgency tactics
✅ Use: Neutral language ("Learn More"), consistent visuals
9.3 Landing Page Rules
Maintain 60/40 content-to-keyword block ratio
Show clear domain branding, no misleading CTAs
Avoid "Read More" buttons, sticky ads, or blended ad/content
9.4 CTA Guidelines
✅ Permitted: "Explore More," "See Options"
❌ Banned: "Apply Now," "Shop Now," "Limited Deals"
9.5 Strict Prohibitions
Misleading offers ("Free car insurance")
Clickbait headlines
Adult/illegal content, trademark abuse
Best Practices
Content Format: Use "Guide to…"/"How to…" articles
First Paragraph: Concise keyword-rich introduction
Keyword Block:
Place prominently (top/sidebar)
Include 5-8 long-tail keywords
Wait 30-60 mins post-publishing for Google indexing
Reporting Note: Data appears only for dimensions with ≥10 clicks
The Future: Survival of the Fittest
Why RSoC Matters:
Aligns with Google’s quality-first approach
Outperforms AFD in UX and RPC
Enables sustainable monetization
Industry Outlook:
Low-quality arbitrage (clickbait/spam) is being eliminated
AI-driven optimization becomes critical
Hybrid strategies (AFD + RSoC) maximize current opportunities
Final Note:
AFD remains viable until its "last click," while RSoC adoption is inevitable. Adaptation and compliance are keys to longevity in search arbitrage.
